ShardingJDBC源码实操(基于Apache Shardingsphere 4.1.0)
序言
数据分片(Shard),是分治模式在存储领域的落地。在高并发、大数据量场景下,数据分片是让服务达到高性能、高可用的常用方案之一。
日常用的存储中间件基本上都有数据分片的实现,比如,
ES中可以把一个索引分成多个分片。每个ES节点可以容纳多个分片,但分片数固定,还有副本,扩容迁移需重建索引;RedisCluster中分成多个节点,每个节点管理一部分哈希槽。集群中有多少主节点,就分成多少片,一个节点负责一个片,扩容迁移直接改变节点和哈希槽的对应关系,并迁移改变对应关系的哈希槽数据;MySQL中的数据分片指的就是分库和分表。这里主要关注两个方面:分片拆分、分片路由。分片拆分包含两方面,表的拆分、库(数据源)的拆分。分片路由包含两方面,库的路由、表的路由。一般业务表和流水表的拆分规则差异较大,业务表一般按照不同业务的流量和容量估算出库表规模做相应拆分(比如128库32表等),而流水表的模式比较固定(比如年库月表、年库日表等)。
接下来,聚焦在MySQL分库分表的实现上。
Shardingjdbc是一种以jar包形式呈现的轻量级MySQL分库分表组件(Client层方案,适用于中小型公司)。
- 优点
- 轻便(不用部署),运维成本低;
- 不需要代理层的二次转发请求,性能很高;
- 对程序员透明,程序员对分库分表逻辑的把控会更强,一旦发生故障,排查问题会比较容易;
- 扩容迁移也可以在确定好要扩容的库表规模后,结合
Shardingjdbc API、Spring动态数据源和动态配置(比如Apollo)来灵活实现。
- 缺点
- 使用会有一定的代码开发工作量,对业务有一些侵入性,如果遇到升级啥的需要各个系统都重新升级版本再发布,各个系统都需要耦合
Shardingjdbc的依赖。
- 使用会有一定的代码开发工作量,对业务有一些侵入性,如果遇到升级啥的需要各个系统都重新升级版本再发布,各个系统都需要耦合
业界常用的还有另一种
Proxy层方案——MyCat。
- 优点
- 和业务代码耦合度很低,只需做一些配置即可,接入成本低,
- 对业务透明,遇到升级之类的在自己中间件这里搞定即可。
- 缺点
- 需要部署,自己运维一套中间件,运维成本高;
- 分库分表逻辑完全由代理中间件管理,对于程序员完全是黑盒,一旦代理本身出问题(比如出错或宕机),会导致无法查询和存储相关业务数据,引发灾难性的后果。
- 适用场景
- 对于大型公司,系统和项目非常多,团队很大,人员充足,那么最好专门弄个人来研究和维护
MyCat,然后大量项目直接透明使用即可。
接下来,聚焦在Shardingjdbc原理上。
Shardingjdbc分库分表的大致流程,如下,
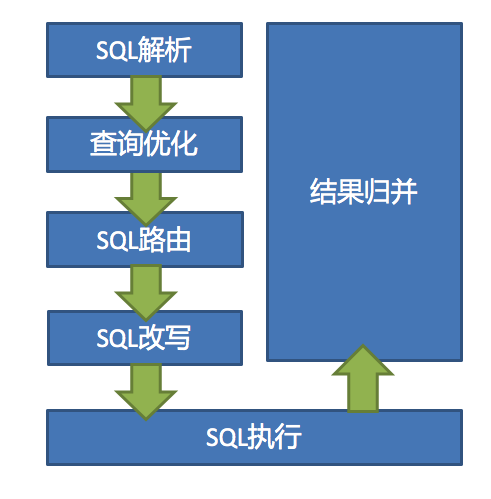
SQL解析 -> 查询优化 ->SQL路由 ->SQL改写 ->SQL执行 -> 结果归并(具体参见shardingjdbc的数据分片-内核剖析-官方文档,包括解析引擎、路由引擎、改写引擎、执行引擎、归并引擎等);- 分库分表后,查询一条
sql,先进行数据源(库)路由,再做表路由。在这个过程中,逻辑表会变成物理表,需要选择合适的分片键(ShardingColumn)、分片策略(ShardingStrategy)和分片算法(ShardingAlgorithm)。
Shardingjdbc相关名词解释
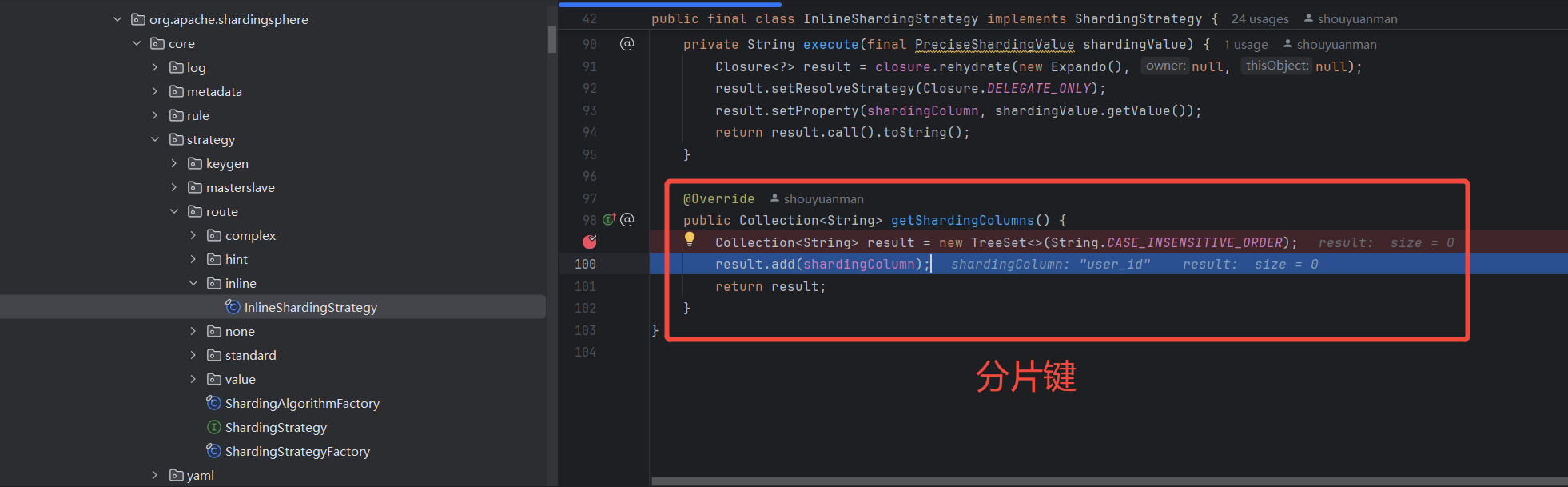
分片键ShardingColumn
用于分片的字段,是将数据库(表)水平拆分的关键字段,支持单字段和多字段分片,比如user_id。在对表中的数据进行分片时,首先要选出一个分片键,一般在业务中经常查询使用的字段会作为分片键。
分片算法ShardingAlgorithm
用于分片的算法,比如PreciseShardingAlgorithm、RangeShardingAlgorithm、ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm等。
具体可以直接翻源码(sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/org/apache/shardingsphere/api/sharding/ShardingAlgorithm.java)。
分片策略ShardingStrategy
分片键和分片算法,统称为分片策略。Shardingjdbc提供5大分片策略,分别是不分片策略(none)、Inline表达式分片策略(inline)、标准分片策略(standard)、复合分片策略(complex)、暗示(强制)分片策略(hint)。
具体可以直接翻源码(sharding-core/sharding-core-common/src/main/java/org/apache/shardingsphere/core/strategy/route/ShardingStrategy.java)。
逻辑表LogicTable
进行水平拆分的时候,同一类型(逻辑、数据结构相同)的表的总称。比如用户数据根据主键尾数取模,拆分为2张表,分别是t_user_0到t_user_1,它们的逻辑表名为t_user。
真实表ActualTable
通过路由算法后,具体映射到的某一个表,就是真实的物理表。即上个示例中的t_user_0和t_user_1。
数据节点DataNode
数据节点是分库分表中一个不可再分的最小数据单元(表),它由数据源名称和数据表组成。比如ds_0.t_user_0,ds_0.t_user_1,ds_1.t_user_0,ds_1.t_user_1,用Groovy表示就是ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}。
广播表BroadcastTable
一个公共表,每个数据源都有一个冗余的数据,表结构和表中的数据在每个数据库中均完全一致,适用于数据量不大且需要与海量数据的表进行关联查询的场景。
一般是字典表或者配置表,某个表一旦被配置为广播表,只要修改某个数据库的广播表,所有数据源中广播表(可以理解为副本)的数据都会跟着同步。
绑定表BindingTable
分片规则一致的主表和子表一般可以建立绑定表关系(两张表均按照同一分片键进行分片),来减少笛卡尔积关联查询导致的没有意义的空查询。
举个主表和子表(比如垂直拆分产生的一对一的主子表,也有其他可能得场景,比如订单主表和订单条目表是一对多的)的例子,将用户表拆分主表和子表,主表中是经常用到的用户主数据(比如昵称),子表中则是不常用到的附加数据(冷数据,比如用户来源渠道)。主表和子表不一定需要建立绑定关系,因场景而异。
动态表DynamicTable
逻辑表和物理表不一定需要在配置规则中静态配置。比如按照日期分片的场景,物理表的名称随着时间的推移会产生变化(流水数据)。
Groovy
一种基于JVM的动态编程语言,形如t_user_$->{user_id % 4},与Java高度兼容,但局限性在于难以维护多层嵌套的业务判断、缺乏类型安全检查、调试困难、性能较差(每次路由都要解释执行)。
在Shardingjdbc中,Groovy只能实现一些简单的Inline表达式分片规则,有些复杂的规则不适用。比如根据订单表的用户ID+订单创建月份+订单类型三个字段组合哈希值进行分片,需要同时满足:
- 历史数据(超过
2年)自动归档到单独分片; VIP用户(用户等级>=3)的订单固定分配到特定高性能节点;- 跨境订单(类型
=overseas)需要路由到符合GDPR合规要求的特殊分片。
这种规则涉及多字段联合计算(哈希算法)、时间维度动态判断、业务属性交叉验证、特殊业务逻辑处理。可以使用下面方案替代,比如ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm、Spring EL表达式(SpEL)、对超复杂场景可考虑自定义分片策略类。
准备测试数据
t_user拆分成2库4表,t_order拆分成2库4表,t_config作为广播表使用,  MySQL数据物料,仅供测试使用
MySQL数据物料,仅供测试使用
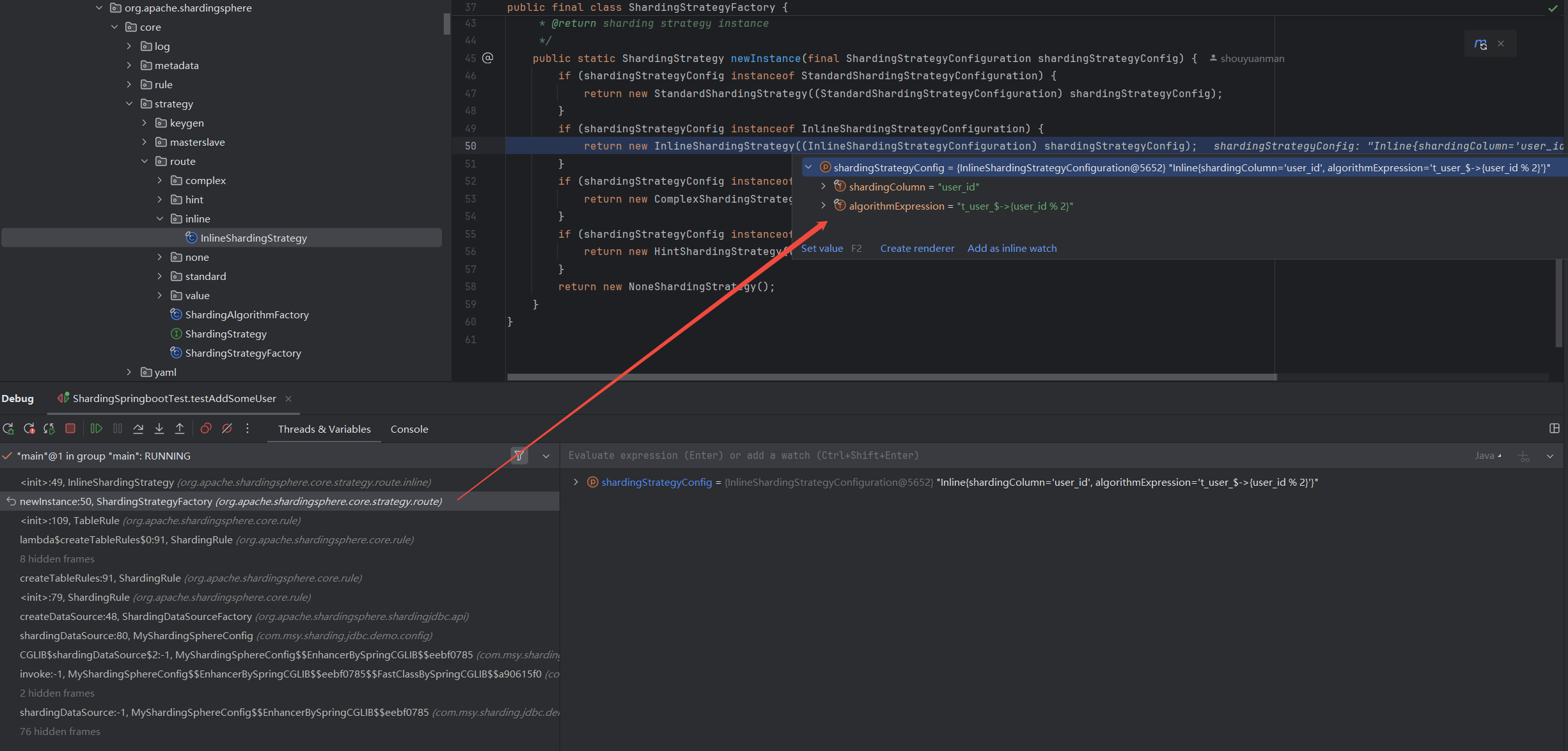
ShardingStrategy
InlineShardingStrategy
从简单的InlineShardingStrategy开始,看Shardingjdbc源码是怎么实现分库分表的。
先构建
MySQL数据源(比如DruidDataSource),如果有多个库,就创建多个,全都添加到DataSourceMap里去,后边创建Sharding超级数据源要用。1 2 3
ds0:sharding_db1 ds1:sharding_db2 // 注:这里ds0和ds1是datasourceName,后边分片时会用到
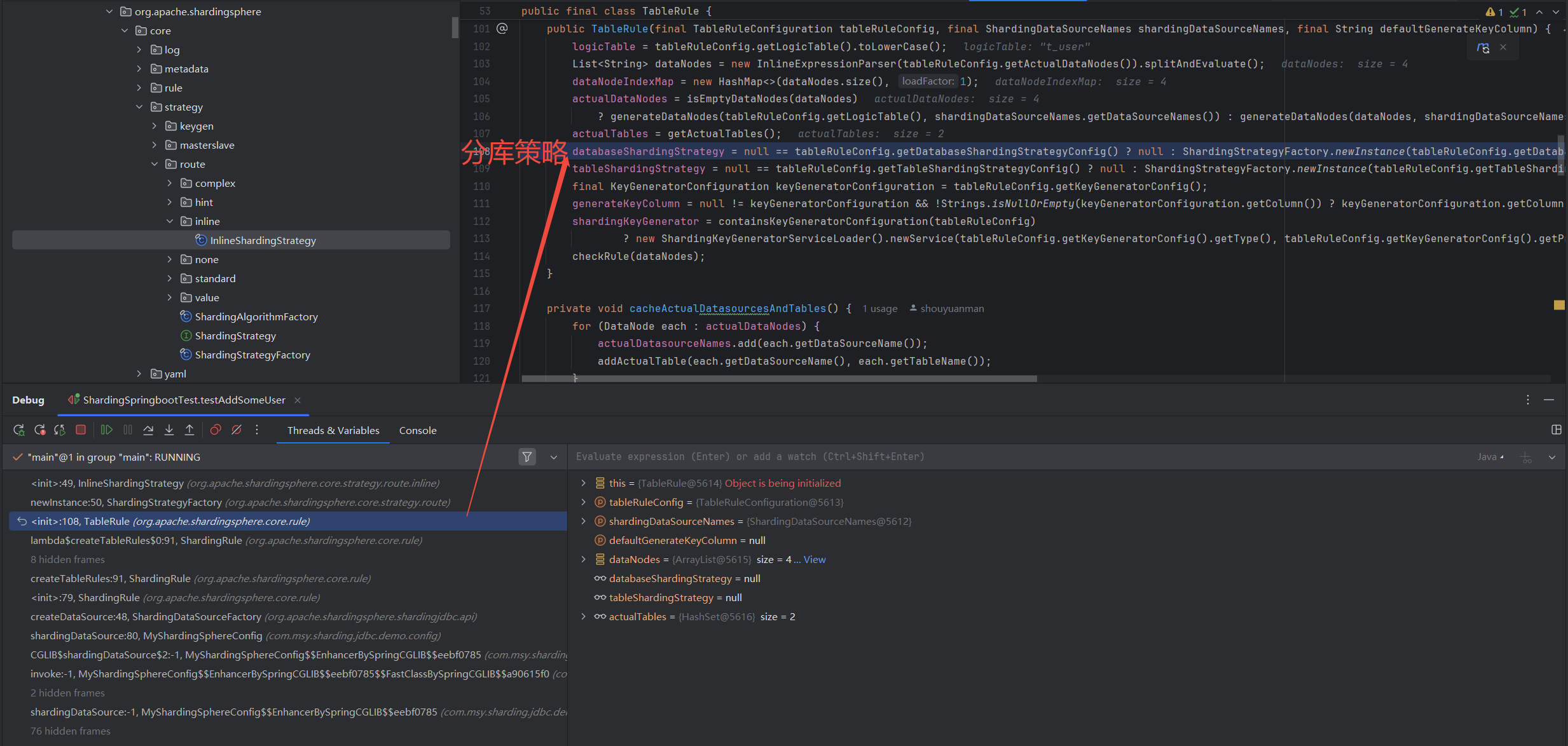
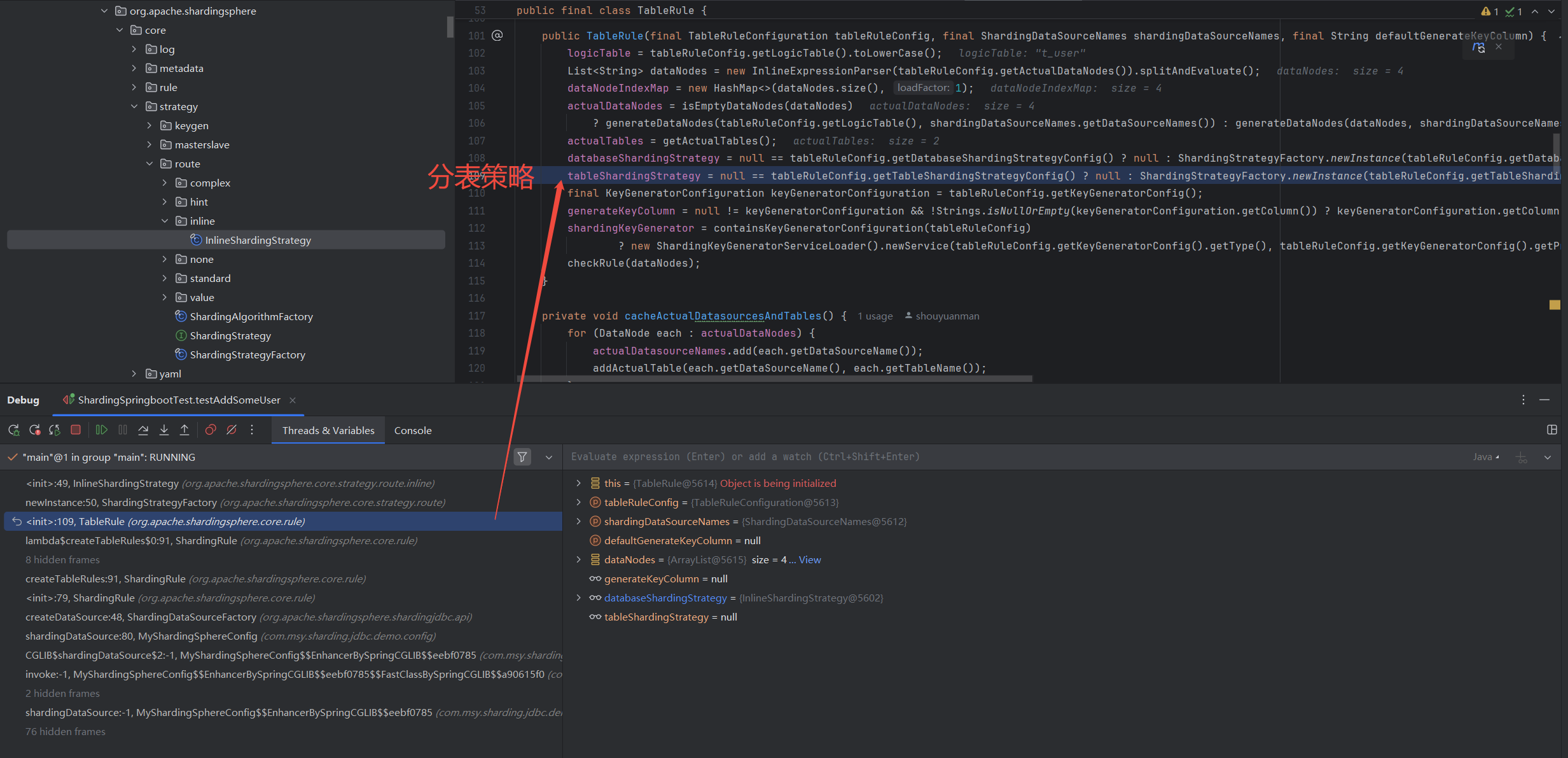
构建分片分表规则,这个阶段主要涉及两个类(
TableRuleConfiguration、ShardingRuleConfiguration),这两个类基本定义了Sharding的具体规则,比如指定逻辑表和真实数据节点,指定分片键、分片算法等。源码中,规则(Rule)大于策略(Strategy),策略大于算法(Algorithm)。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79
// sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/ // org/apache/shardingsphere/api/config/sharding/strategy/ // InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration.java // Inline Sharding分片策略配置 public final class InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration implements ShardingStrategyConfiguration { // 分片键 private final String shardingColumn; // 分片算法 private final String algorithmExpression; public InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration(final String shardingColumn, final String algorithmExpression) { Preconditions.checkArgument(!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(shardingColumn), "ShardingColumn is required."); Preconditions.checkArgument(!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(algorithmExpression), "AlgorithmExpression is required."); this.shardingColumn = shardingColumn; this.algorithmExpression = algorithmExpression; } @Override public String toString() { return "Inline{" + "shardingColumn='" + shardingColumn + '\'' + ", algorithmExpression='" + algorithmExpression + '\'' + '}'; } } // sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/ // org/apache/shardingsphere/api/config/sharding/ // TableRuleConfiguration.java // 分库分表的配置类 public final class TableRuleConfiguration { // 逻辑表,比如t_user private final String logicTable; // 真实数据节点,比如ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1} private final String actualDataNodes; // 分库规则,比如new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("user_id", "ds${user_id % 2}") private ShardingStrategyConfiguration databaseShardingStrategyConfig; // 分表规则,比如new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("user_id", "t_user_$->{user_id % 2}") private ShardingStrategyConfiguration tableShardingStrategyConfig; // 主键ID生成规则,比如new KeyGeneratorConfiguration("SNOWFLAKE", "user_id", properties) private KeyGeneratorConfiguration keyGeneratorConfig; public TableRuleConfiguration(final String logicTable) { this(logicTable, null); } public TableRuleConfiguration(final String logicTable, final String actualDataNodes) { Preconditions.checkArgument(!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(logicTable), "LogicTable is required."); this.logicTable = logicTable; this.actualDataNodes = actualDataNodes; } } // sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/ // org/apache/shardingsphere/api/config/sharding/ // ShardingRuleConfiguration.java // Sharding规则的配置类,包括除一般分库分表外的绑定表、广播表、主从规则等 public final class ShardingRuleConfiguration implements RuleConfiguration { // 分库分表规则 private Collection<TableRuleConfiguration> tableRuleConfigs = new LinkedList<>(); // 绑定表 private Collection<String> bindingTableGroups = new LinkedList<>(); // 广播表 private Collection<String> broadcastTables = new LinkedList<>(); // 多数据源一定得指定默认数据源,只有一个数据源就不需要指定 private String defaultDataSourceName; private ShardingStrategyConfiguration defaultDatabaseShardingStrategyConfig; private ShardingStrategyConfiguration defaultTableShardingStrategyConfig; private KeyGeneratorConfiguration defaultKeyGeneratorConfig; // 主从规则 private Collection<MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration> masterSlaveRuleConfigs = new LinkedList<>(); // encrypt规则 private EncryptRuleConfiguration encryptRuleConfig; }
配置基础属性,构建超级数据源。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
// sharding-jdbc/sharding-jdbc-core/src/main/java/ // org/apache/shardingsphere/shardingjdbc/api/ // ShardingDataSourceFactory.java // Shardingjdbc封装过的数据源 @NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) public final class ShardingDataSourceFactory { /** * Create sharding data source. * * @param dataSourceMap data source map * @param shardingRuleConfig rule configuration for databases and tables sharding * @param props properties for data source * @return sharding data source * @throws SQLException SQL exception */ public static DataSource createDataSource( final Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap, final ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfig, final Properties props) throws SQLException { return new ShardingDataSource(dataSourceMap, new ShardingRule(shardingRuleConfig, dataSourceMap.keySet()), props); } }
有了超级数据源后,就能做业务的增删改查了。
上面是Shardingjdbc实现的基本流程原理,使用properties配置文件来配置实现,如下所示,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds0,ds1
// ......
// 使用配置文件方式,虽然比较简单,但不方便动态在线扩容,这里仅作演示。
// 实际项目中,做分片规则和数据源配置时,
// 常用结合Shardingjdbc API、Spring动态数据源和动态配置(比如Apollo或者ZooKeeper等),
// 一起实现Shardingjdbc分库分表,便于后期动态扩容。
//
// Shardingjdbc中有配置中心,虽然也能对数据源做切换,但效果不太好,新老版本变化还很大,不推荐使用。
// 具体参考:https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/4.1.0/cn/features/orchestration/config-center/
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user_$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
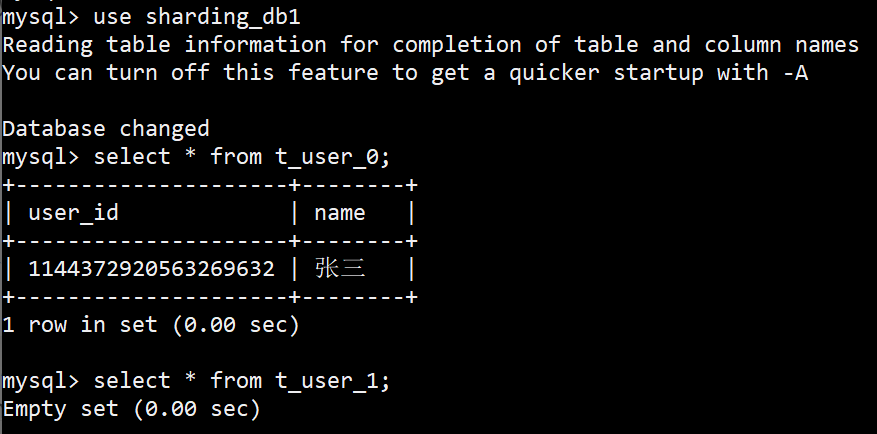
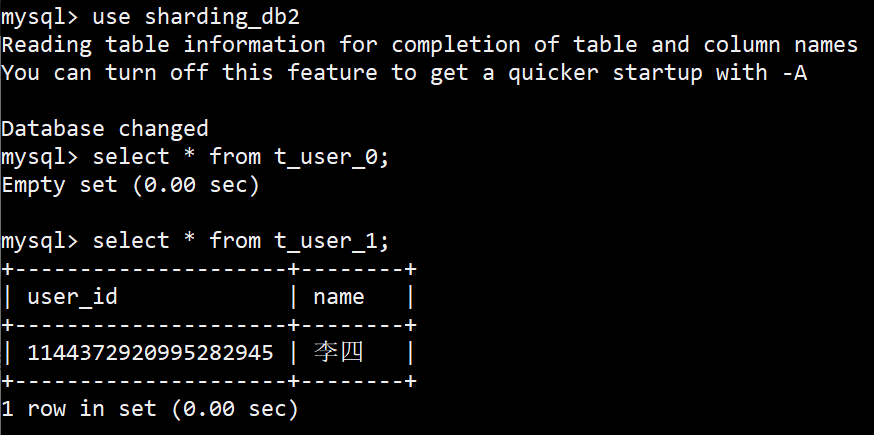
配置好后,可以用Case实际测试,比如,现在我要插入两条数据,
1
2
name='张三'
name='李四'
测试插入数据,观察具体执行时的分片键和分片策略,如下,
代码执行时的数据源、具体ShardingRule配置、基础属性配置等,打印如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-1} inited
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-2} inited
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - ShardingRuleConfiguration:
defaultDataSourceName: ds0
tables:
t_user:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: ds${user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
keyGenerator:
column: user_id
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_user
tableStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: t_user_$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - Properties:
sql.show: 'true'
逻辑表sql,以及路由到对应的真实表sql,都能看到,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-metadata - Loading 1 logic tables' meta data.
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-metadata - Loading 9 tables' meta data.
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-metadata - Meta data load finished, cost 84 milliseconds.
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_user(name) values('张三')
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@24a298a6, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@982bb90), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@982bb90, columnNames=[name], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=0, valueExpressions=[LiteralExpressionSegment(startIndex=32, stopIndex=35, literals=张三), DerivedLiteralExpressionSegment(super=LiteralExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, literals=1144372920563269632))], parameters=[])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=user_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144372920563269632])])
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_user_0(name, user_id) values('张三', 1144372920563269632)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_user(name) values('李四')
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@4d0b0fd4, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@7a24eb3), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@7a24eb3, columnNames=[name], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=0, valueExpressions=[LiteralExpressionSegment(startIndex=32, stopIndex=35, literals=李四), DerivedLiteralExpressionSegment(super=LiteralExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, literals=1144372920995282945))], parameters=[])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=user_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144372920995282945])])
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_user_1(name, user_id) values('李四', 1144372920995282945)
DB里边的数据,也符合预期。
InlineShardingStrategy在使用时比较简单,不需要自定义分片算法,直接在配置文件中用Groovy表达式写规则,它支持对SQL语句中的=和IN的分片操作,但只支持单分片键。
该策略通常用于精准分片(PreciseShardingAlgorithm,含有IN、=的分片),使用起来极致简洁,但不能支持范围分片(RangeShardingAlgorithm,含有BETWEEN AND、>、>=、<=、<的分片)。
StandardShardingStrategy
更常用,比InlineSharding复杂一点,但能解决更多的问题,比如范围分片。其中,配置时,PreciseShardingAlgorithm是必选项,RangeShardingAlgorithm是可选项。
配置示例,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
# 范围分片算法,可选配置
# spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.RangeOrderShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
# 范围分片算法,可选配置
# spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.RangeOrderShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
StandardShardingStrategy对应的配置类,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public final class StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration implements ShardingStrategyConfiguration {
// 分片键
private final String shardingColumn;
// 精准分片算法
private final PreciseShardingAlgorithm preciseShardingAlgorithm;
// 范围分片算法
private final RangeShardingAlgorithm rangeShardingAlgorithm;
public StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration(final String shardingColumn, final PreciseShardingAlgorithm preciseShardingAlgorithm) {
this(shardingColumn, preciseShardingAlgorithm, null);
}
public StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration(final String shardingColumn, final PreciseShardingAlgorithm preciseShardingAlgorithm, final RangeShardingAlgorithm rangeShardingAlgorithm) {
Preconditions.checkArgument(!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(shardingColumn), "ShardingColumns is required.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(preciseShardingAlgorithm, "PreciseShardingAlgorithm is required.");
this.shardingColumn = shardingColumn;
this.preciseShardingAlgorithm = preciseShardingAlgorithm;
this.rangeShardingAlgorithm = rangeShardingAlgorithm;
}
}
看下PreciseShardingAlgorithm和RangeShardingAlgorithm的代码实现,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
// 精准分片算法
public interface PreciseShardingAlgorithm<T extends Comparable<?>> extends ShardingAlgorithm {
/**
* Sharding.
*
* @param availableTargetNames available data sources or tables's names
* @param shardingValue sharding value
* @return sharding result for data source or table's name
*/
String doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, PreciseShardingValue<T> shardingValue);
}
// sharding-jdbc/sharding-jdbc-core/src/test/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/shardingjdbc/fixture/
// PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm.java 实现
public final class PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public String doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final PreciseShardingValue<Integer> shardingValue) {
for (String each : availableTargetNames) {
if (each.endsWith(String.valueOf(shardingValue.getValue() % 2))) {
return each;
}
}
return null;
}
}
// 范围分片算法
public interface RangeShardingAlgorithm<T extends Comparable<?>> extends ShardingAlgorithm {
/**
* Sharding.
*
* @param availableTargetNames available data sources or tables's names
* @param shardingValue sharding value
* @return sharding results for data sources or tables's names
*/
Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, RangeShardingValue<T> shardingValue);
}
// sharding-jdbc/sharding-jdbc-core/src/test/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/shardingjdbc/fixture/
// RangeOrderShardingAlgorithm.java 实现
public final class RangeOrderShardingAlgorithm implements RangeShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final RangeShardingValue<Integer> shardingValue) {
Collection<String> result = new HashSet<>(2);
for (int i = shardingValue.getValueRange().lowerEndpoint(); i <= shardingValue.getValueRange().upperEndpoint(); i++) {
for (String each : availableTargetNames) {
if (each.endsWith(String.valueOf(i % 2))) {
result.add(each);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
测试StandardSharding中精准分片的效果,
1
2
-- 精准分片
select * from t_user where user_id in (10,11,23)
同一条sql命中了哪些库、哪些表,命中的库表之间做笛卡尔积路由,
1
2
3
4
5
6
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: select * from t_user where user_id in (10,11,23)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: SelectStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.SelectStatement@4e93dcb9, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@188b6035), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@188b6035, projectionsContext=ProjectionsContext(startIndex=7, stopIndex=7, distinctRow=false, projections=[ShorthandProjection(owner=Optional.empty, actualColumns=[ColumnProjection(owner=null, name=user_id, alias=Optional.empty), ColumnProjection(owner=null, name=name, alias=Optional.empty)])]), groupByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.groupby.GroupByContext@4a34e9f, orderByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.orderby.OrderByContext@6f6621e3, paginationContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.pagination.PaginationContext@3fc05ea2, containsSubquery=false)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: select * from t_user_0 where user_id in (10,11,23)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: select * from t_user_1 where user_id in (10,11,23)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select * from t_user_0 where user_id in (10,11,23)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select * from t_user_1 where user_id in (10,11,23)
具体查询时,分片路由的日志打印,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
shardingValue = 10 target = ds0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 0
// 10 命中了 ds0,直接返回
shardingValue = 11 target = ds0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
// 11 没命中了 ds0,进入下次迭代
shardingValue = 11 target = ds1 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
// 11 命中了 ds1,直接返回
// 以下同理,
shardingValue = 23 target = ds0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 23 target = ds1 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 10 target = t_user_0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 0
shardingValue = 11 target = t_user_0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 11 target = t_user_1 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 23 target = t_user_0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 23 target = t_user_1 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 10 target = t_user_0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 0
shardingValue = 11 target = t_user_0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 11 target = t_user_1 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 23 target = t_user_0 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
shardingValue = 23 target = t_user_1 shardingValue.getValue() % 2) = 1
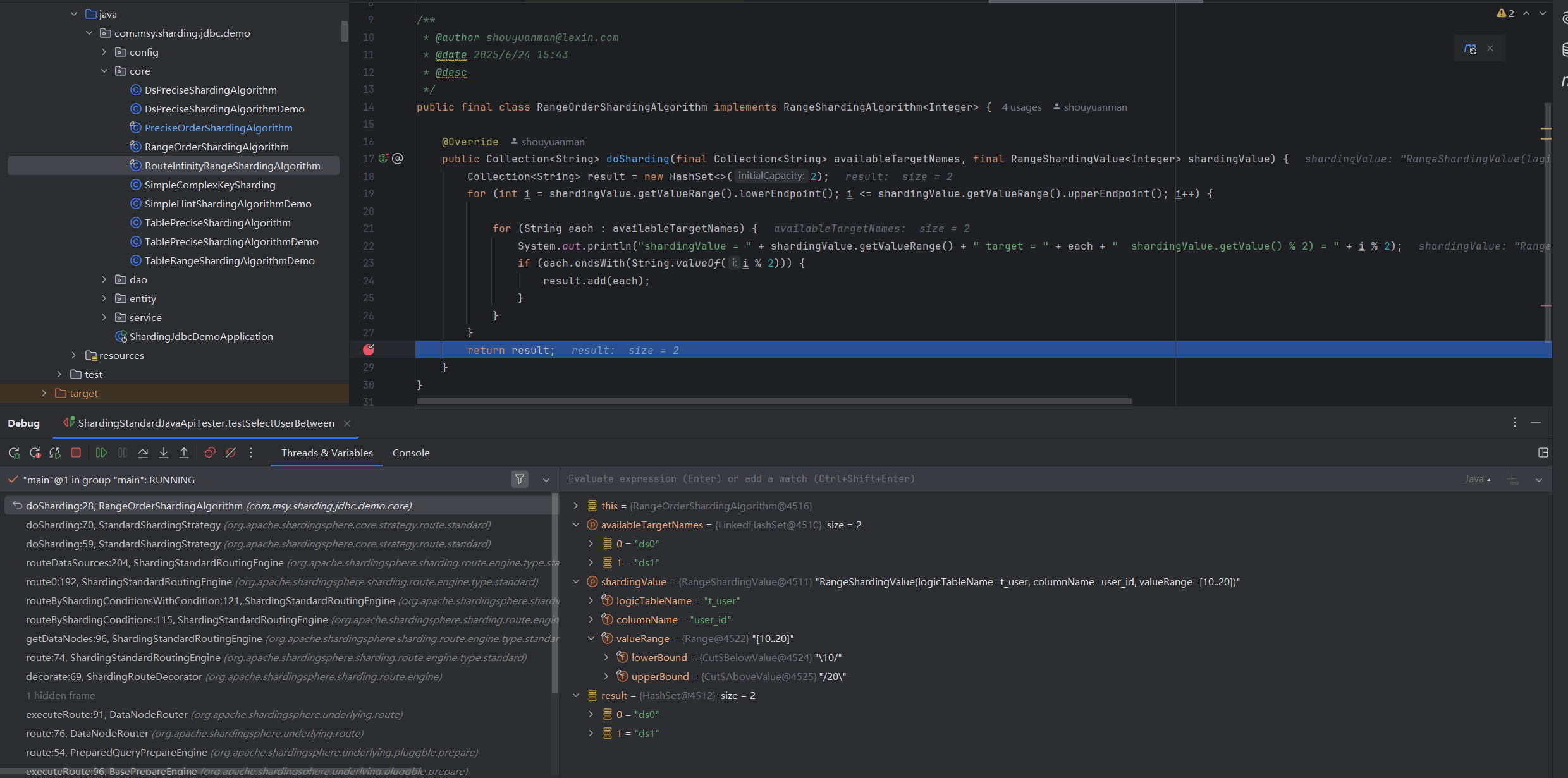
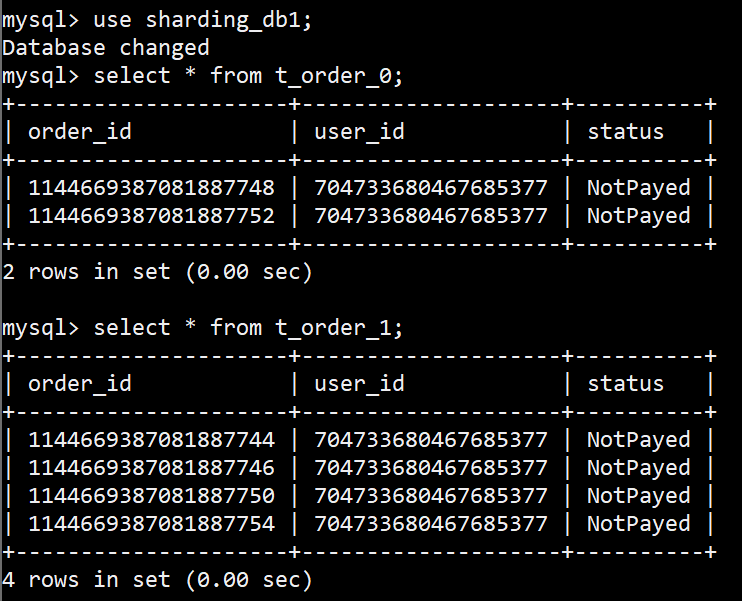
观察具体执行时的分片键,以及shardingValue路由映射到的库表,如下,
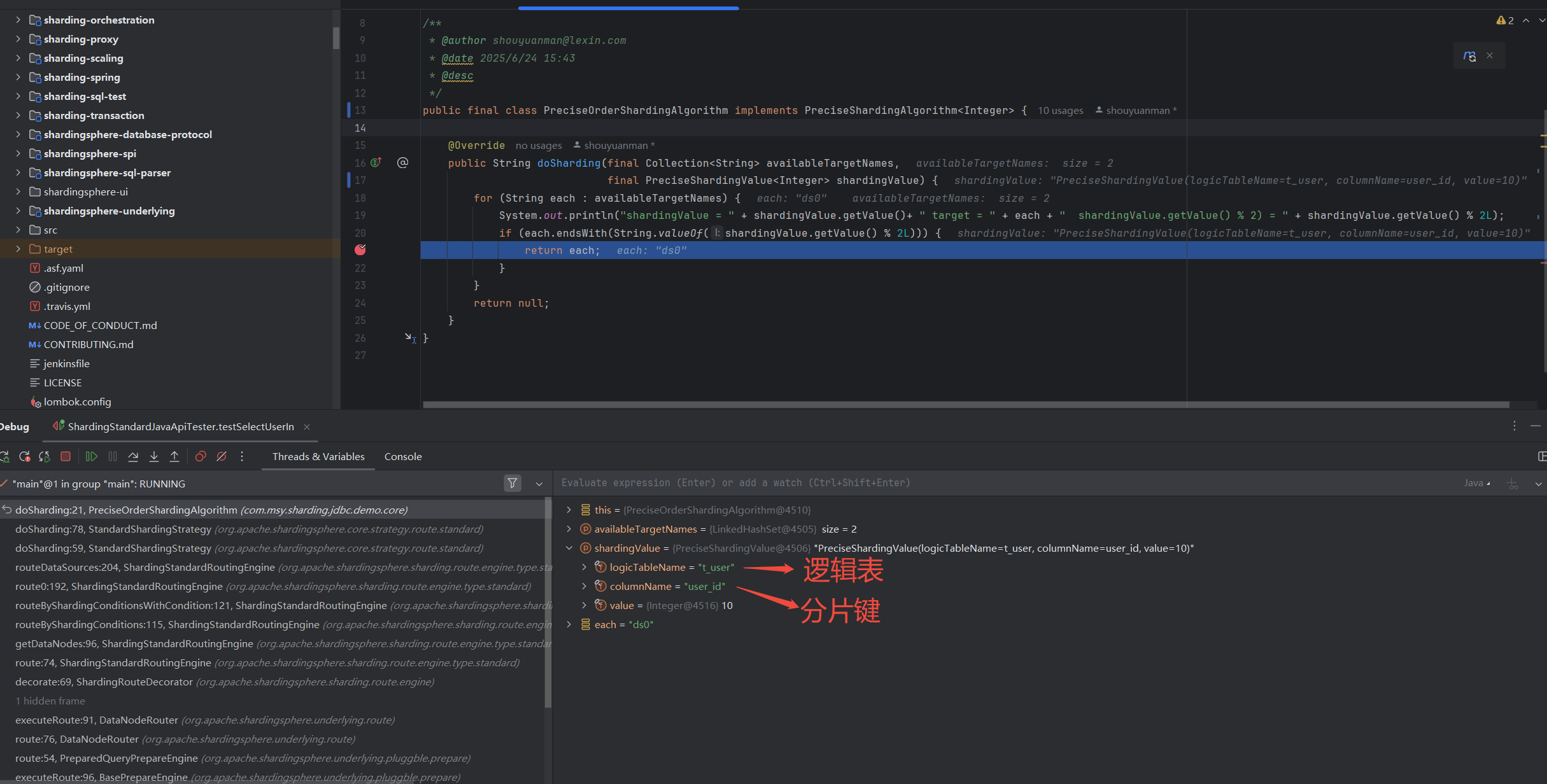 StandardShardingStrategy 分库路由 示例1
StandardShardingStrategy 分库路由 示例1
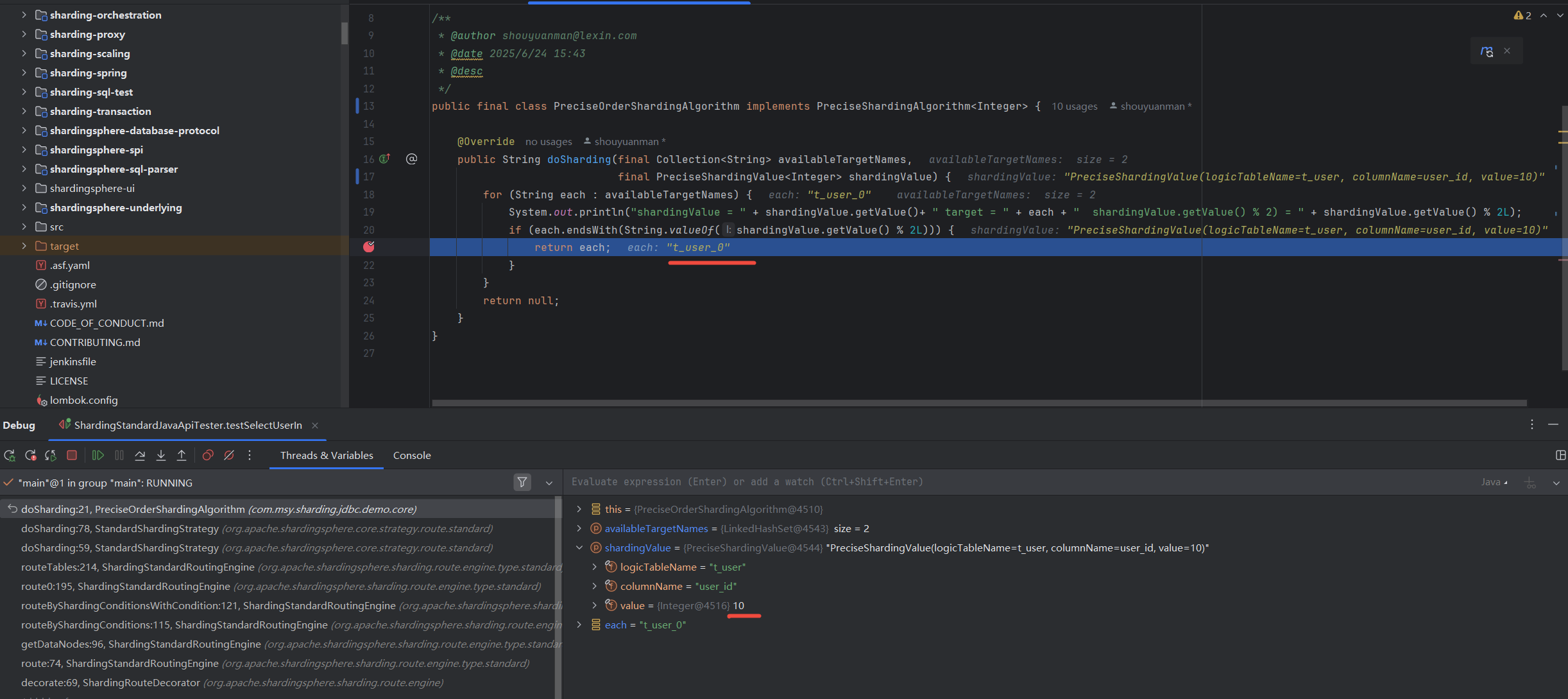 StandardShardingStrategy 分表路由 示例1
StandardShardingStrategy 分表路由 示例1
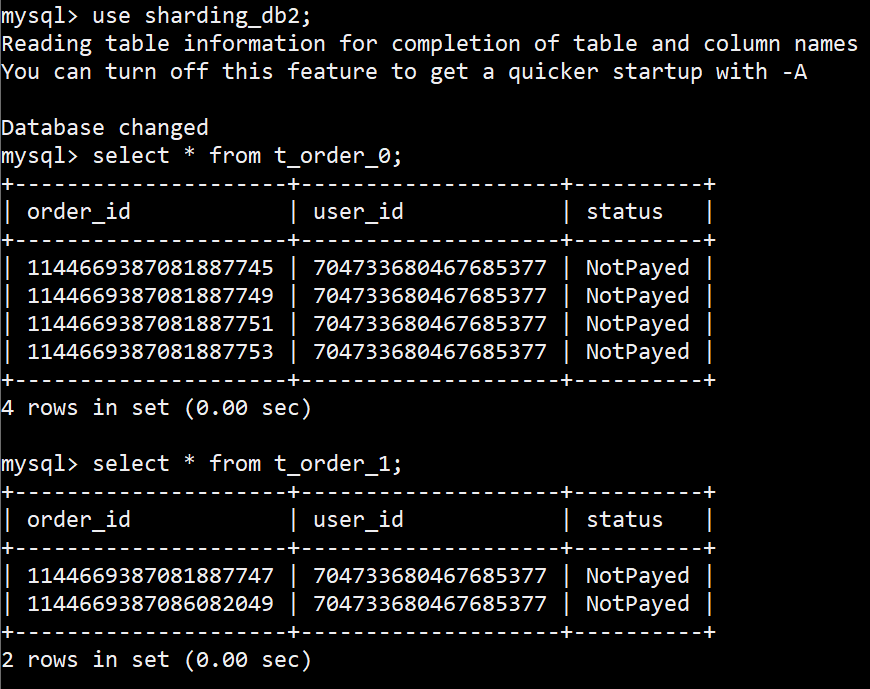
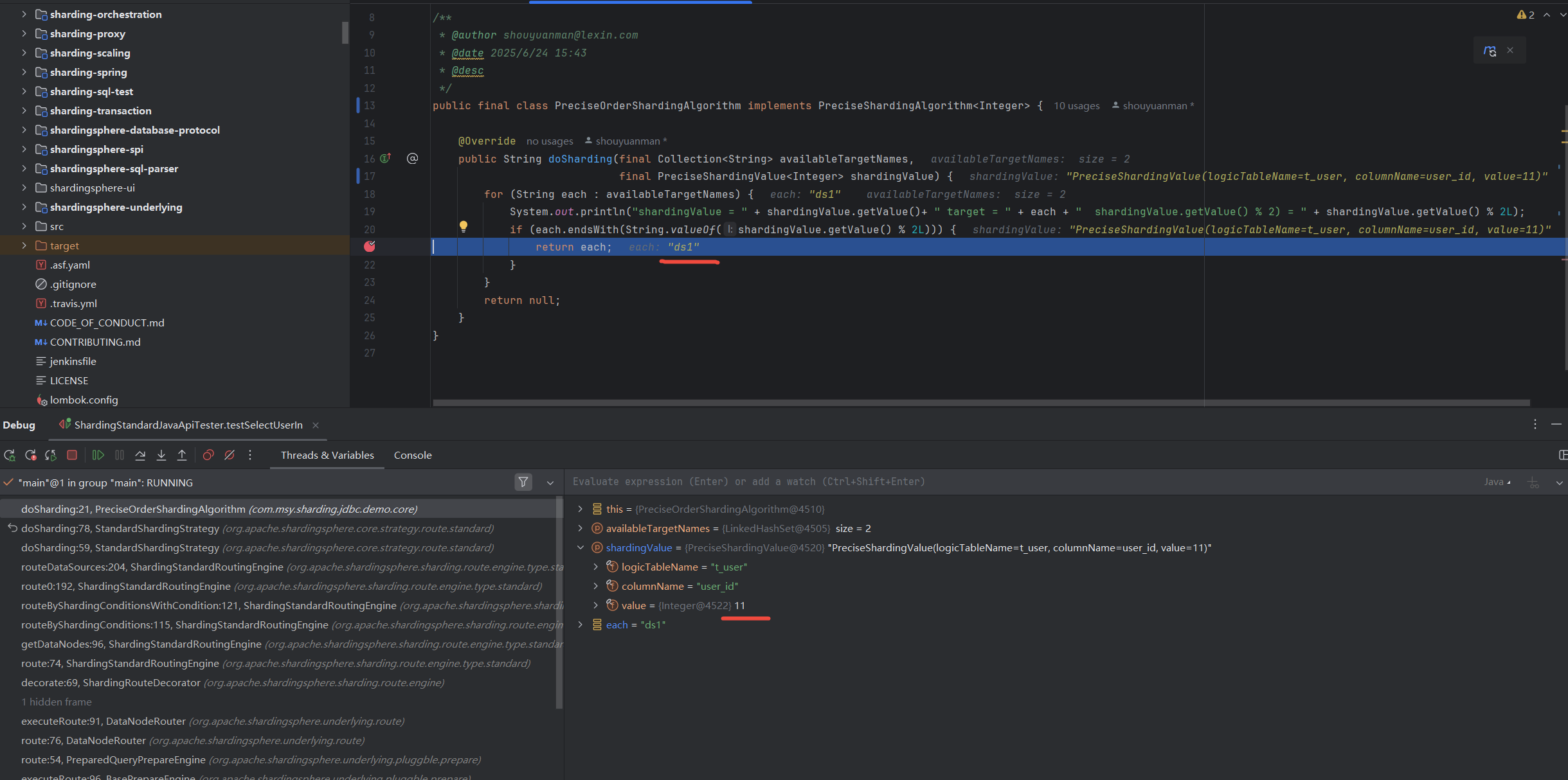 StandardShardingStrategy 分库路由 示例2
StandardShardingStrategy 分库路由 示例2
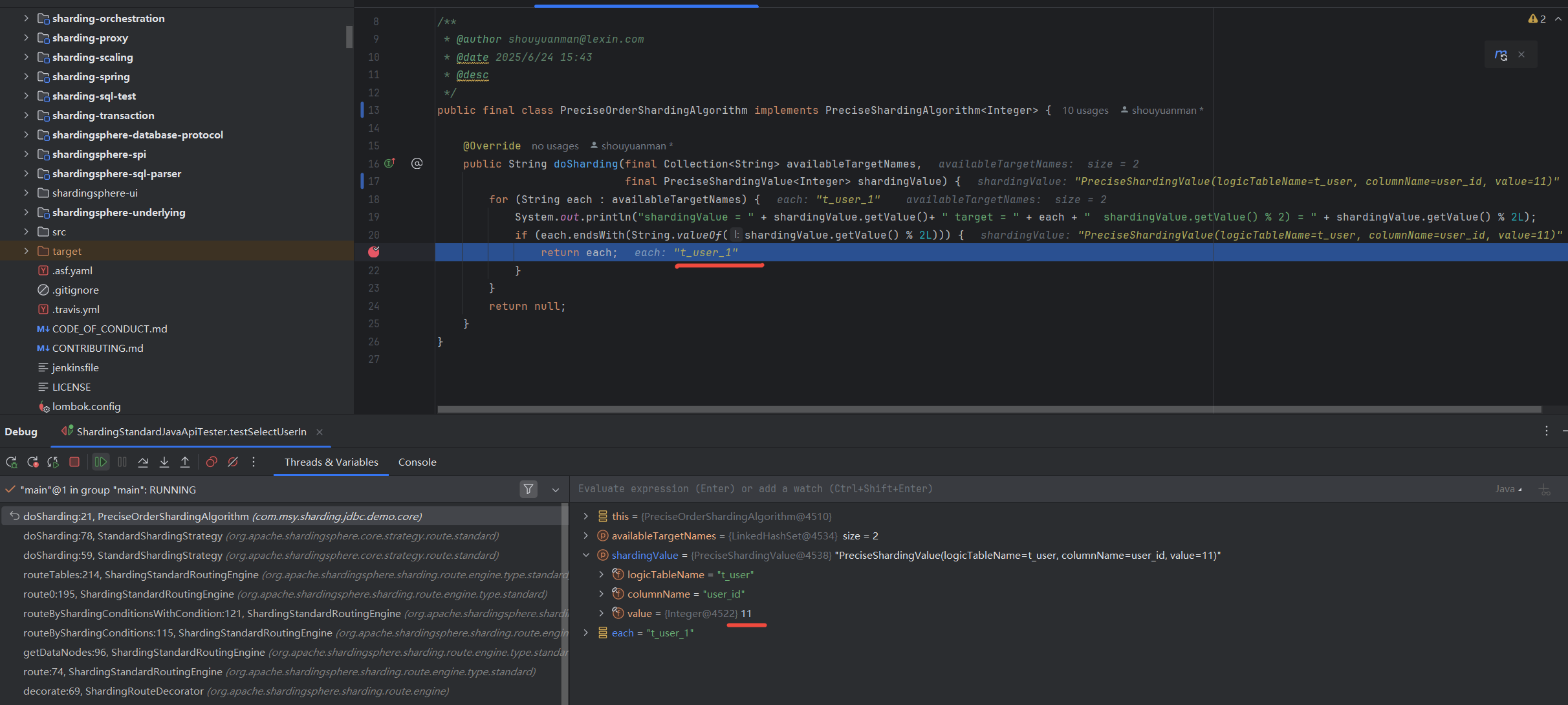 StandardShardingStrategy 分表路由 示例2
StandardShardingStrategy 分表路由 示例2
测试StandardSharding中范围分片的效果,
1
2
-- 范围分片
select * from t_user where user_id between 10 and 20
同样地,同一条sql语句命中了哪些库、哪些表,命中的库表之间做笛卡尔积路由,
1
2
3
4
5
6
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: select * from t_user where user_id between 10 and 20
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: SelectStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.SelectStatement@3bd3d05e, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@6aba5d30), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@6aba5d30, projectionsContext=ProjectionsContext(startIndex=7, stopIndex=7, distinctRow=false, projections=[ShorthandProjection(owner=Optional.empty, actualColumns=[ColumnProjection(owner=null, name=user_id, alias=Optional.empty), ColumnProjection(owner=null, name=name, alias=Optional.empty)])]), groupByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.groupby.GroupByContext@61d34b4, orderByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.orderby.OrderByContext@588307f7, paginationContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.pagination.PaginationContext@7df76d99, containsSubquery=false)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: select * from t_user_0 where user_id between 10 and 20
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: select * from t_user_1 where user_id between 10 and 20
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select * from t_user_0 where user_id between 10 and 20
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select * from t_user_1 where user_id between 10 and 20
StandardSharding分库分表规则,结果如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-1} inited
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-2} inited
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - ShardingRuleConfiguration:
broadcastTables:
- t_config
defaultDataSourceName: ds0
tables:
t_user:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
standard:
preciseAlgorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
rangeAlgorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.RangeOrderShardingAlgorithm
shardingColumn: user_id
keyGenerator:
column: user_id
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_user
tableStrategy:
standard:
preciseAlgorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
rangeAlgorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.RangeOrderShardingAlgorithm
shardingColumn: user_id
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - Properties:
sql.show: 'true'
注意,StandardSharding的结果,返回的是一个集合(不同于精准分片,返回的是一个值)。
ComplexShardingStrategy
InlineSharding和StandardSharding的不足,就是只有一个分片键。如果多个分片键参与分片路由,就得用ComplexShardingStrategy。它同样支持对SQL语句中的=,>,<,>=,<=,IN和BETWEEN AND的分片操作。
ComplexShardingStrategy支持多分片键,由于多分片键之间的关系复杂,因此并未进行过多的封装,而是直接将分片键值组合以及分片操作符透传至分片算法,具体分片细节完全由应用开发者实现,提供最大的灵活度。
配置示例,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.complex.sharding-columns=order_id,user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.SimpleComplexKeySharding
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=order_id
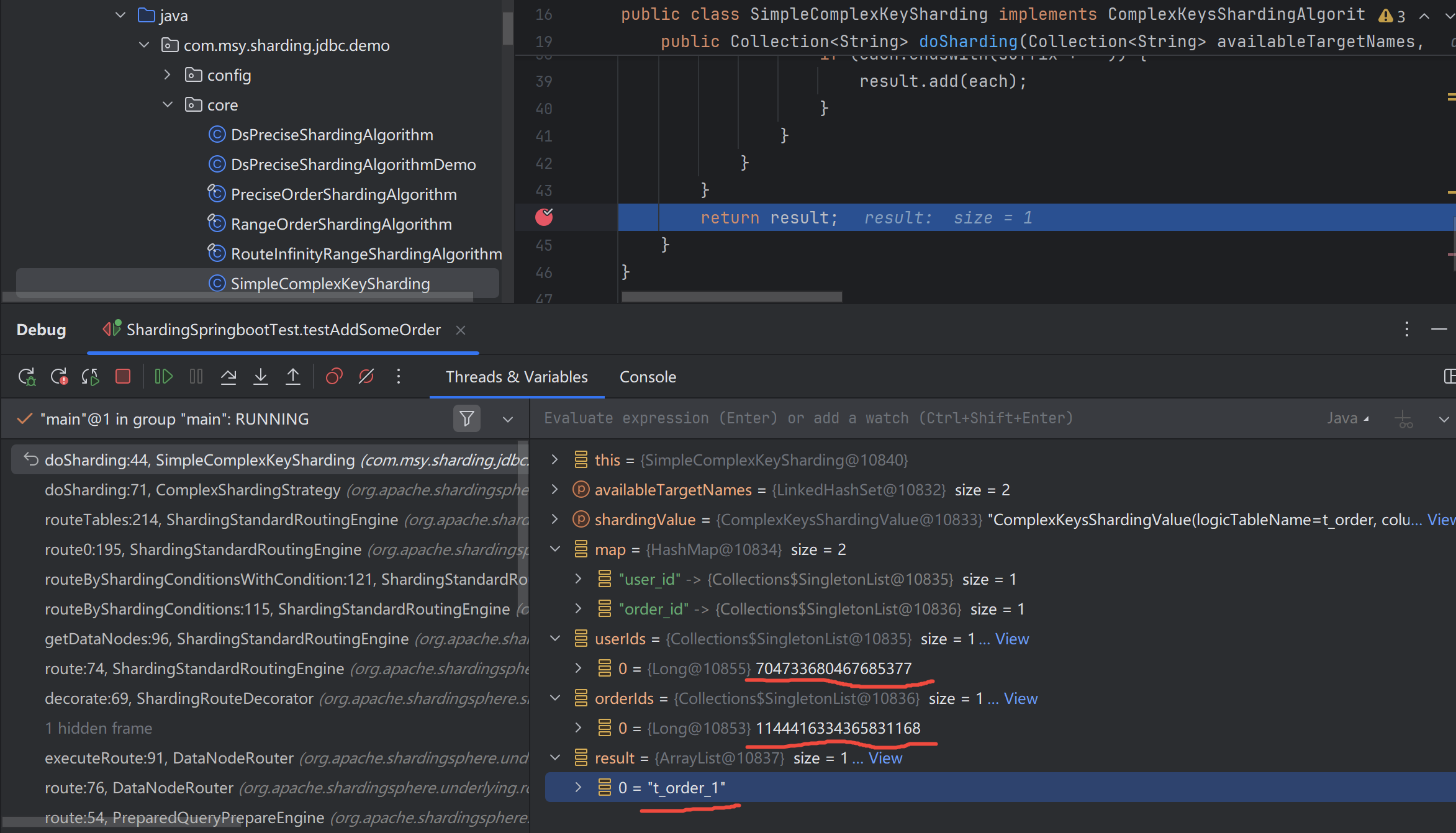
测试ComplexSharding效果,
1
insert into t_order (status, user_id) values ('NotPayed', 704733680467685377L)
看下ComplexShardingStrategy的源码实现,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
// sharding-core/sharding-core-common/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/core/strategy/route/complex/
// ComplexShardingStrategy.java 实现
public final class ComplexShardingStrategy implements ShardingStrategy {
@Getter
// 分片键
private final Collection<String> shardingColumns;
// 具体分片细节完全由应用开发者实现,
// 直接将分片键值组合以及分片操作符透传至分片算法
private final ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm shardingAlgorithm;
public ComplexShardingStrategy(final ComplexShardingStrategyConfiguration complexShardingStrategyConfig) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(complexShardingStrategyConfig.getShardingColumns(), "Sharding columns cannot be null.");
Preconditions.checkNotNull(complexShardingStrategyConfig.getShardingAlgorithm(), "Sharding algorithm cannot be null.");
shardingColumns = new TreeSet<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
shardingColumns.addAll(Splitter.on(",").trimResults().splitToList(complexShardingStrategyConfig.getShardingColumns()));
shardingAlgorithm = complexShardingStrategyConfig.getShardingAlgorithm();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final Collection<RouteValue> shardingValues, final ConfigurationProperties properties) {
Map<String, Collection<Comparable<?>>> columnShardingValues = new HashMap<>(shardingValues.size(), 1);
Map<String, Range<Comparable<?>>> columnRangeValues = new HashMap<>(shardingValues.size(), 1);
String logicTableName = "";
for (RouteValue each : shardingValues) {
if (each instanceof ListRouteValue) {
columnShardingValues.put(each.getColumnName(), ((ListRouteValue) each).getValues());
} else if (each instanceof RangeRouteValue) {
columnRangeValues.put(each.getColumnName(), ((RangeRouteValue) each).getValueRange());
}
logicTableName = each.getTableName();
}
Collection<String> shardingResult = shardingAlgorithm.doSharding(availableTargetNames, new ComplexKeysShardingValue(logicTableName, columnShardingValues, columnRangeValues));
Collection<String> result = new TreeSet<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
result.addAll(shardingResult);
return result;
}
}
// sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/api/sharding/complex/
// ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm.java 接口
public interface ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<T extends Comparable<?>> extends ShardingAlgorithm {
/**
* Sharding.
*
* @param availableTargetNames available data sources or tables's names
* @param shardingValue sharding value
* @return sharding results for data sources or tables's names
*/
Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, ComplexKeysShardingValue<T> shardingValue);
}
// sharding-core/sharding-core-common/src/test/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/core/shard/fixture/
// ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithmFixture.java
// 随便挑出来一个ComplexShardingAlgorithm的实现实例
public final class ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithmFixture implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final ComplexKeysShardingValue<Integer> shardingValue) {
return availableTargetNames;
}
}
// sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/api/sharding/complex/
// ComplexKeysShardingValue.java 实现
public final class ComplexKeysShardingValue<T extends Comparable<?>> implements ShardingValue {
// 逻辑表
private final String logicTableName;
// 精准分片ShardingValue
private final Map<String, Collection<T>> columnNameAndShardingValuesMap;
// 范围分片ShardingValue
private final Map<String, Range<T>> columnNameAndRangeValuesMap;
}
ComplexSharding分库分表规则,结果如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-1} inited
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-2} inited
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - ShardingRuleConfiguration:
bindingTables:
- t_order,t_user
broadcastTables:
- t_config
tables:
t_user:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: ds$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
keyGenerator:
column: user_id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_user
tableStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: t_user_$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
standard:
preciseAlgorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
shardingColumn: order_id
keyGenerator:
column: order_id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_order
tableStrategy:
complex:
algorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.SimpleComplexKeySharding
shardingColumns: order_id,user_id
t_config:
keyGenerator:
column: id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_config
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - Properties:
sql.show: 'true'
库表路由Case,如下,
1
2
3
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@ab11e76, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@6a0d47e8), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@6a0d47e8, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144417867002261504])])
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377L, 1144417867002261504]
观察具体执行时的分片键,以及shardingValue路由映射到的库表,如下,
HintShardingStrategy
前面的分片策略都是解析SQL语句,提取分片键和分片值,并根据设置的分片算法进行分片,是Apache ShardingSphere对SQL零侵入的实现方式。若SQL语句中没有分片条件,则无法进行分片,需要全路由。
分片值不存在于SQL,而是在外部业务逻辑里,使用外部值分片,需要用程序另行指定。比如根据月份或者天数,甚至看心情分片,这就叫HintShardingStrategy。
看下HintShardingStrategy的源码实现,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
// sharding-core/sharding-core-common/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/core/strategy/route/hint/
// HintShardingStrategy.java
public final class HintShardingStrategy implements ShardingStrategy {
@Getter
// 分片键
private final Collection<String> shardingColumns;
// 分片算法
private final HintShardingAlgorithm shardingAlgorithm;
public HintShardingStrategy(final HintShardingStrategyConfiguration hintShardingStrategyConfig) {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(hintShardingStrategyConfig.getShardingAlgorithm(), "Sharding algorithm cannot be null.");
shardingColumns = new TreeSet<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
shardingAlgorithm = hintShardingStrategyConfig.getShardingAlgorithm();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final Collection<RouteValue> shardingValues, final ConfigurationProperties properties) {
ListRouteValue shardingValue = (ListRouteValue) shardingValues.iterator().next();
Collection<String> shardingResult = shardingAlgorithm.doSharding(availableTargetNames,
new HintShardingValue(shardingValue.getTableName(), shardingValue.getColumnName(), shardingValue.getValues()));
Collection<String> result = new TreeSet<>(String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
result.addAll(shardingResult);
return result;
}
}
// sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/api/sharding/hint/
// HintShardingAlgorithm.java
public interface HintShardingAlgorithm<T extends Comparable<?>> extends ShardingAlgorithm {
/**
* Sharding.
*
* <p>sharding value injected by hint, not in SQL.</p>
*
* @param availableTargetNames available data sources or tables's names
* @param shardingValue sharding value
* @return sharding result for data sources or tables's names
*/
Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> availableTargetNames, HintShardingValue<T> shardingValue);
}
// 一个默认的HintSharding算法实现,
// 相当于笛卡尔积路由,还不如用NoneSharding(后边会有)
// 一般使用时会根据需求自定义ShardingAlgorithm(自定义ShardingValue的用法)
public final class DefaultHintShardingAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final HintShardingValue<Integer> shardingValue) {
return availableTargetNames;
}
}
// sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/api/sharding/hint/
// HintShardingValue.java
// Hint算法里边的ShardingValue是用HintManager传递到ShardingStrategy来的
public final class HintShardingValue<T extends Comparable<?>> implements ShardingValue {
// 逻辑表
private final String logicTableName;
// 分片键
private final String columnName;
// 分片值
private final Collection<T> values;
}
测试HintSharding,配置如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.SimpleHintShardingAlgorithmDemo
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=order_id
HintSharding算法:通过编程的方式向HintManager中添加分片值,该分片值仅在当前线程内生效;然后通过指定hint暗示策略 + hint暗示算法分片的配置来使用前面传进来的ShardingValue(传递链路后面有)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// 自定义ShardingValue是怎么传到ShardingStrategy和ShardingAlgorithm那的
for (int month = 1; month <= 12; month++) {
final int index = month;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("当前月份: {}", index);
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("t_order", index);
hintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue("t_order", index);
Order dto = new Order();
dto.setUserId(704733680467685377L);
//增加订单
entityService.addOrder(dto);
hintManager.close();
}
}).start();
}
// 自定义ShardingAlgorithm
if (each.endsWith(String.valueOf(shardingValue % 2))) {
result.add(each);
}
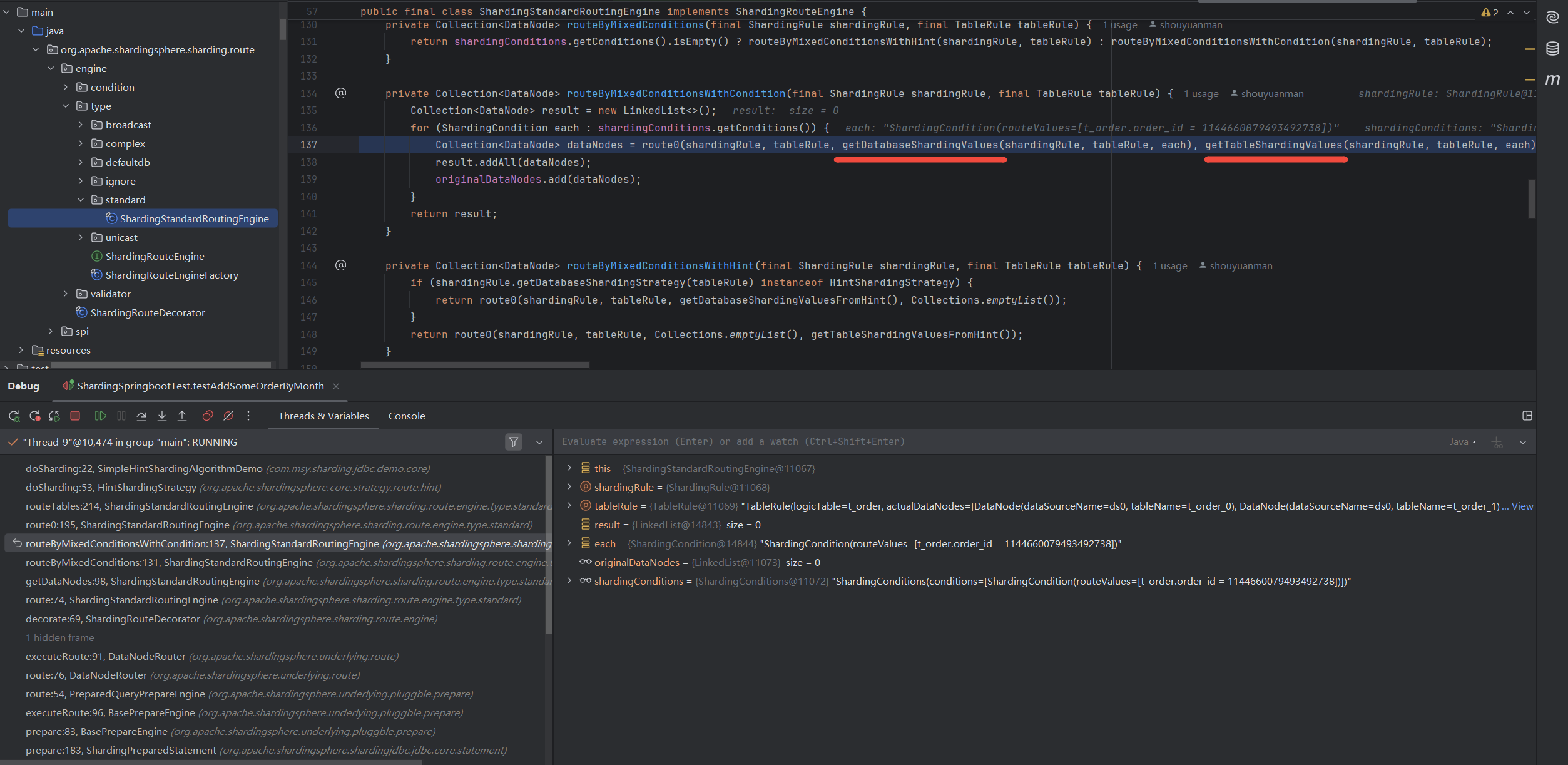
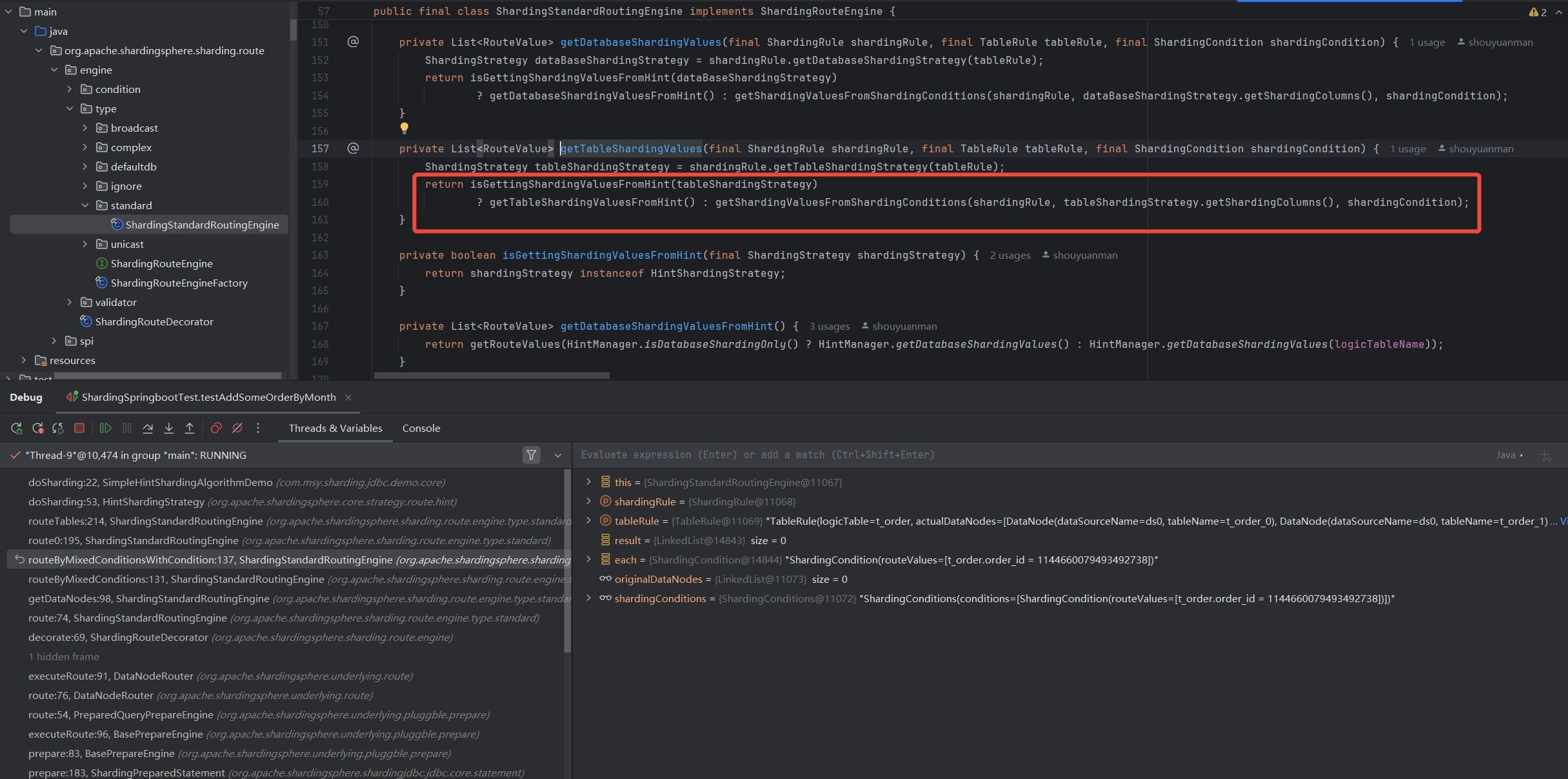
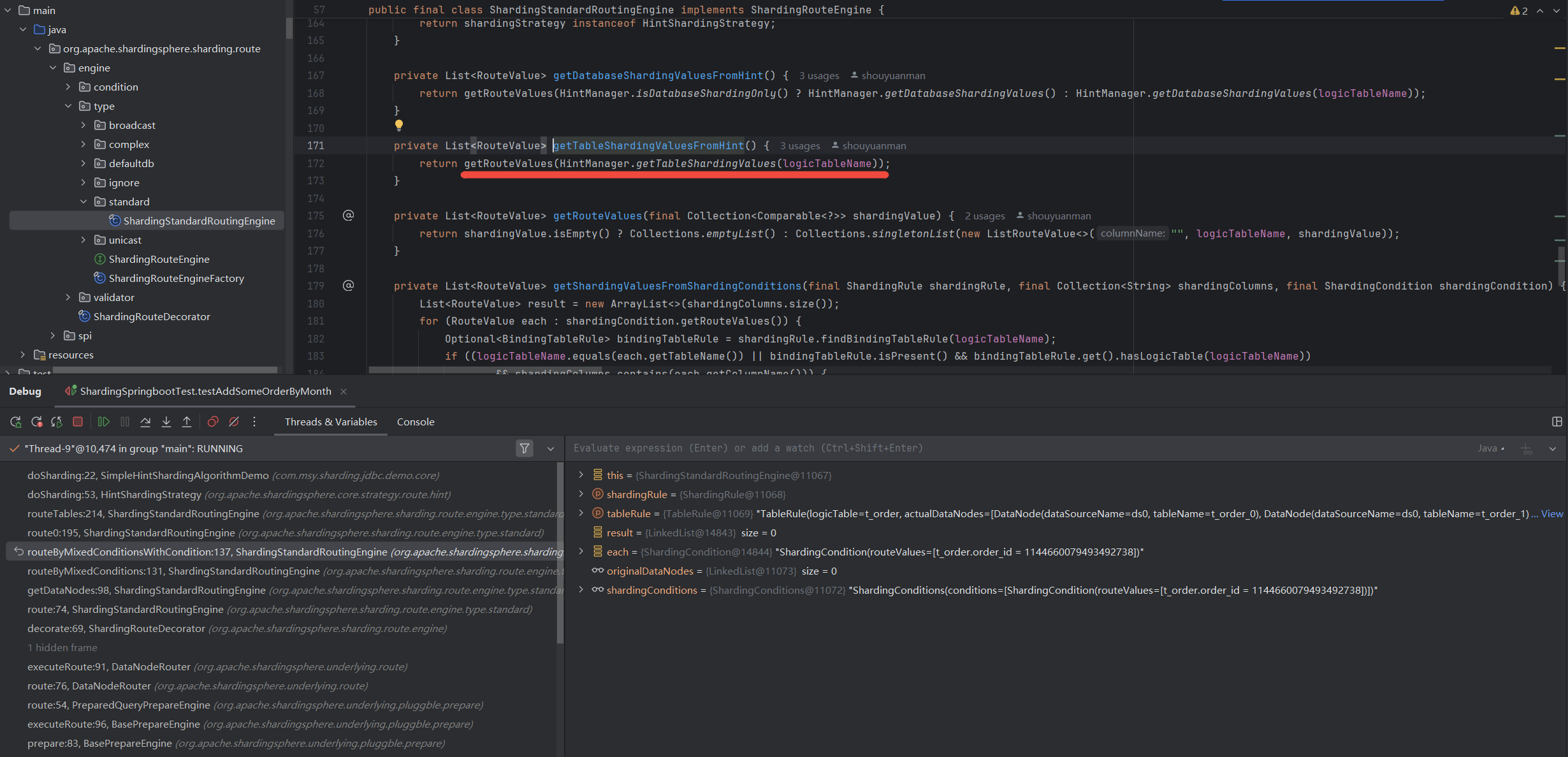
观察HintManager传递ShardingValue到ShardingStrategy里的链路,
这里是获得
ShardingValue的地方,如果识别到
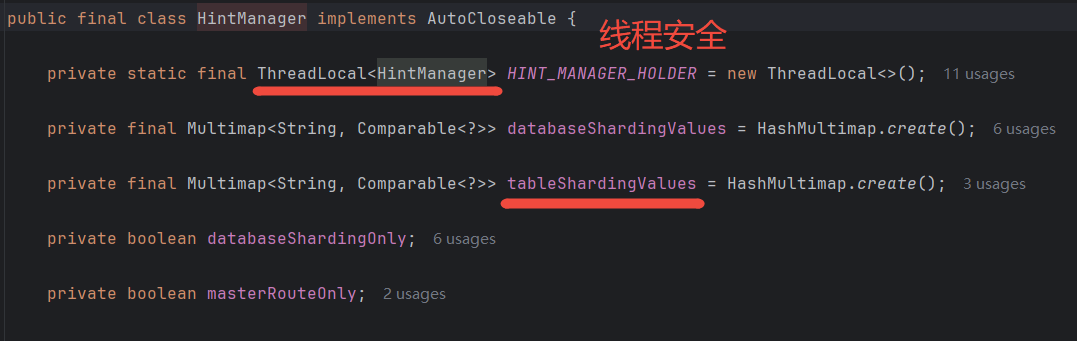
HintSharding,就去get,getShardingValue是直接根据logicTable从HintManager的tableShardingValue,可以看到
HintManager是线程安全的。
运行观察分库分表的具体规则,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-1} inited
[main] INFO c.a.druid.pool.DruidDataSource - {dataSource-2} inited
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - ShardingRuleConfiguration:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
standard:
preciseAlgorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.PreciseOrderShardingAlgorithm
shardingColumn: order_id
keyGenerator:
column: order_id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_order
tableStrategy:
hint:
algorithmClassName: com.msy.sharding.jdbc.demo.core.SimpleHintShardingAlgorithmDemo
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - Properties:
sql.show: 'true'
数据根据SharingAlgorithm路由到物理表,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[Thread-3] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-13] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-4] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-8] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-10] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-11] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-12] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-14] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-9] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-6] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-5] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-7] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_order (status, user_id) values (?, ?)
[Thread-8] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@2b6e3b68, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@78faeff8), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@78faeff8, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887753])])
[Thread-3] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@36ef41d6, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@5d7ad5e), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@5d7ad5e, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887754])])
[Thread-13] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@6cad3b58, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@743c8a17), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@743c8a17, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887746])])
[Thread-11] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@477b7b2b, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@18f5b3d4), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@18f5b3d4, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887747])])
[Thread-9] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@4e7db0d, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@7229d265), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@7229d265, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887750])])
[Thread-4] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@53152d9a, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@3fa6a187), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@3fa6a187, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887749])])
[Thread-7] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@1be3afd5, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@1de753), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@1de753, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387086082049])])
[Thread-5] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@73e0d849, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@5b3bfa22), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@5b3bfa22, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887744])])
[Thread-10] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@71683cf8, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@32d5e1d), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@32d5e1d, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887751])])
[Thread-6] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@4c6acfa2, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@7d89f508), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@7d89f508, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887748])])
[Thread-3] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887754]
[Thread-13] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887746]
[Thread-7] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387086082049]
[Thread-12] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@114d6f82, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@47e1c518), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@47e1c518, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887752])])
[Thread-14] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@2aac1258, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@163bbc3d), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@163bbc3d, columnNames=[status, user_id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=46, stopIndex=46, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=49, stopIndex=49, parameterMarkerIndex=1), DerivedParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(super=ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=0, stopIndex=0, parameterMarkerIndex=2))], parameters=[NotPayed, 704733680467685377])], generatedKeyContext=Optional[GeneratedKeyContext(columnName=order_id, generated=true, generatedValues=[1144669387081887745])])
[Thread-8] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_order_0 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887753]
[Thread-11] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887747]
[Thread-9] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887750]
[Thread-6] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_0 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887748]
[Thread-4] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_order_0 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887749]
[Thread-5] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_1 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887744]
[Thread-12] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_order_0 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887752]
[Thread-10] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_order_0 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887751]
[Thread-14] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_order_0 (status, user_id, order_id) values (?, ?, ?) ::: [NotPayed, 704733680467685377, 1144669387081887745]
观察DB数据,符合预期,
NoneShardingStrategy
NoneShardingStrategy中的数据会查询(或插入)每个库每张表(全路由),可以理解为广播表。
看下NoneShardingStrategy的源码实现,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// sharding-core/sharding-core-common/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/core/strategy/route/none/
// NoneShardingStrategy.java
public final class NoneShardingStrategy implements ShardingStrategy {
// NoneShardingStrategy没有对应ShardingAlgorithm
private final Collection<String> shardingColumns = Collections.emptyList();
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final Collection<RouteValue> shardingValues, final ConfigurationProperties properties) {
// 这里相当于全路由
return availableTargetNames;
}
}
// sharding-core/sharding-core-api/src/main/java/
// org/apache/shardingsphere/api/config/sharding/strategy/
// NoneShardingStrategyConfiguration.java
public final class NoneShardingStrategyConfiguration implements ShardingStrategyConfiguration {
// 空空如也
}
配置如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.none=true
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.none=true
运行查询case,观察分库分表的具体规则,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
none: ''
keyGenerator:
column: order_id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_order
tableStrategy:
none: ''
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - Properties:
sql.show: 'true'
逻辑查询sql,会全路由到物理表,
1
2
3
4
5
6
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: select order_id , status, user_id from t_order where order_id=?
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: SelectStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.SelectStatement@23acd55e, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@eaf3dd0), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@eaf3dd0, projectionsContext=ProjectionsContext(startIndex=7, stopIndex=115, distinctRow=false, projections=[ColumnProjection(owner=orderentit0_, name=order_id, alias=Optional[order_id1_1_]), ColumnProjection(owner=orderentit0_, name=status, alias=Optional[status2_1_]), ColumnProjection(owner=orderentit0_, name=user_id, alias=Optional[user_id3_1_])]), groupByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.groupby.GroupByContext@5add0cc0, orderByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.orderby.OrderByContext@5b04224a, paginationContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.pagination.PaginationContext@1e470a51, containsSubquery=false)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: select order_id, status, user_id from t_order_0 where order_id=? ::: [1144669387081887749]
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: select order_id, status, user_id from t_order_1 where order_id=? ::: [1144669387081887749]
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select order_id, status, user_id from t_order_0 where order_id=? ::: [1144669387081887749]
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select order_id, status, user_id from t_order_1 where order_id=? ::: [1144669387081887749]
广播表
看下broadcastTables的源码实现,broadcastTables所处的位置和tableRuleConfigs分库分表规则在同一级,都在ShardingRuleConfiguration下边,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public final class ShardingRuleConfiguration implements RuleConfiguration {
private Collection<TableRuleConfiguration> tableRuleConfigs = new LinkedList<>();
private Collection<String> bindingTableGroups = new LinkedList<>();
private Collection<String> broadcastTables = new LinkedList<>();
private String defaultDataSourceName;
private ShardingStrategyConfiguration defaultDatabaseShardingStrategyConfig;
private ShardingStrategyConfiguration defaultTableShardingStrategyConfig;
private KeyGeneratorConfiguration defaultKeyGeneratorConfig;
private Collection<MasterSlaveRuleConfiguration> masterSlaveRuleConfigs = new LinkedList<>();
private EncryptRuleConfiguration encryptRuleConfig;
}
配置如下,
1
2
// 如果不配置广播表属性,不管插入还是查询,都只路由到一个数据源里边
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=t_config
观察广播表的具体规则,如下,
1
2
broadcastTables:
- t_config
插入一条数据,会全路由广播,如下,
1
2
3
4
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: insert into t_config (status, id) values (?, ?)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: InsertStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.InsertStatement@16a89351, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@395854dd), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@395854dd, columnNames=[status, id], insertValueContexts=[InsertValueContext(parametersCount=2, valueExpressions=[ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=42, stopIndex=42, parameterMarkerIndex=0), ParameterMarkerExpressionSegment(startIndex=45, stopIndex=45, parameterMarkerIndex=1)], parameters=[UN_KNOWN, 3])], generatedKeyContext=Optional.empty)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds0 ::: insert into t_config (status, id) values (?, ?) ::: [UN_KNOWN, 3]
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: insert into t_config (status, id) values (?, ?) ::: [UN_KNOWN, 3]
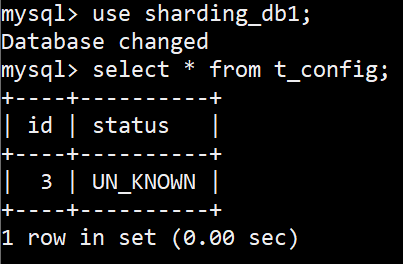
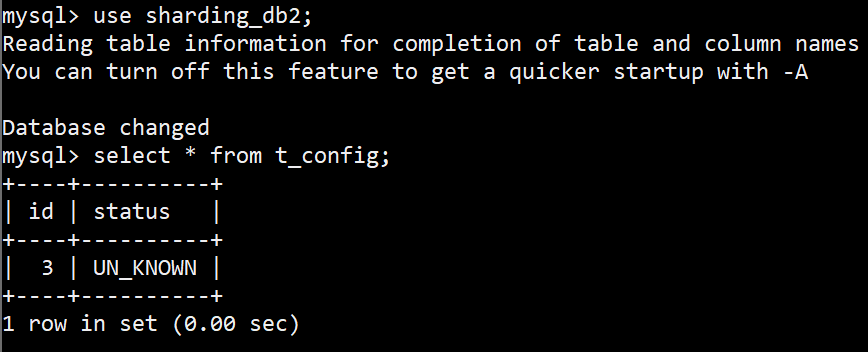
再看下查询,只路由到一个库,
1
2
3
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: select id, status from t_config limit ?
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: SelectStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.SelectStatement@315bb2bb, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@57e35236), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@57e35236, projectionsContext=ProjectionsContext(startIndex=7, stopIndex=66, distinctRow=false, projections=[ColumnProjection(owner=configenti0_, name=id, alias=Optional[id1_0_]), ColumnProjection(owner=configenti0_, name=status, alias=Optional[status2_0_])]), groupByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.groupby.GroupByContext@7c9015c6, orderByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.orderby.OrderByContext@36b2b6e6, paginationContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.pagination.PaginationContext@5a9004e1, containsSubquery=false)
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: select id, status from t_config limit ? ::: [3]
绑定表
假设同一个用户的所有订单都分在同一个片,可以使用绑定表。
配置如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_user_$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=t_order_$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key-generator.props.worker.id=123
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.binding-tables[0]=t_order,t_user
观察绑定表的具体规则,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
[main] INFO o.a.s.c.l.ConfigurationLogger - ShardingRuleConfiguration:
bindingTables:
- t_order,t_user
tables:
t_user:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: ds$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
keyGenerator:
column: user_id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_user
tableStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: t_user_$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{0..1}
databaseStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: ds$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
keyGenerator:
column: order_id
props:
worker.id: '123'
type: SNOWFLAKE
logicTable: t_order
tableStrategy:
inline:
algorithmExpression: t_order_$->{user_id % 2}
shardingColumn: user_id
看下绑定表的查询效果,消除了无效的空查询,如下,
1
2
3
4
5
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Logic SQL: SELECT a.* FROM `t_order` a left join `t_user` b on a.user_id=b.user_id where a.user_id=?
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - SQLStatement: SelectStatementContext(super=CommonSQLStatementContext(sqlStatement=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.sql.statement.dml.SelectStatement@aeb8ee2, tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@320ca97c), tablesContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.table.TablesContext@320ca97c, projectionsContext=ProjectionsContext(startIndex=7, stopIndex=9, distinctRow=false, projections=[ShorthandProjection(owner=Optional[a], actualColumns=[ColumnProjection(owner=a, name=order_id, alias=Optional.empty), ColumnProjection(owner=a, name=user_id, alias=Optional.empty), ColumnProjection(owner=a, name=status, alias=Optional.empty)])]), groupByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.groupby.GroupByContext@3c592c0c, orderByContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.orderby.OrderByContext@3979c6e8, paginationContext=org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.binder.segment.select.pagination.PaginationContext@6fb3d3bb, containsSubquery=false)
// 如果不设置绑定表关系,t_order_1会同时和t_user_0、t_user_1做关联查询
// 这里做了绑定后,会消除t_order_1和t_user_0的绑定关系
[main] INFO ShardingSphere-SQL - Actual SQL: ds1 ::: SELECT a.* FROM `t_order_1` a left join `t_user_1` b on a.user_id=b.user_id where a.user_id=? ::: [704733680467685377]
附录
shardingjdbc的SQL执行流程
回顾做
jdbc开发时,涉及到了哪些接口?
- 需要到
DataSource,通过DataSource获取Connection;- 定义一条
SQL,通过Connection获取Prepared Statement,执行SQL语句,关闭连接;- 这些都定义在
java.sql基础包里边。
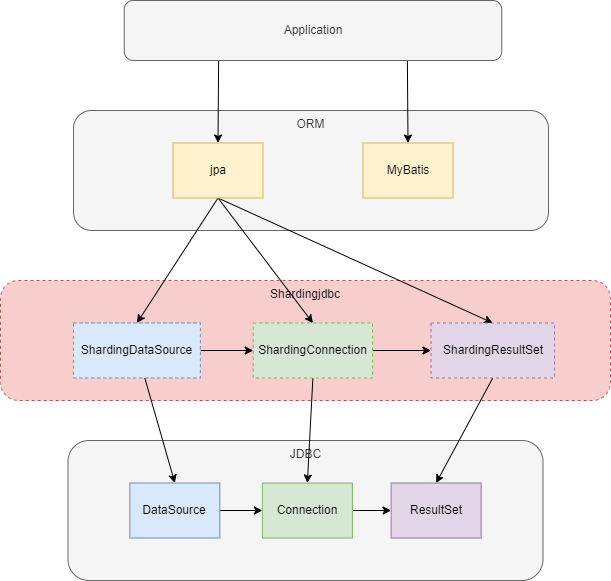
shardingjdbc对原有的DataSource、Connection等接口扩展成ShardingDataSource、ShardingConnection,而对外暴露的分片操作接口与JDBC规范中所提供的接口完全一致,只要你熟悉JDBC就可以轻松应用shardingjdbc来实现分库分表。实际使用的时候,替换掉shardingjdbc的数据源就可以了。
ShardingDataSource继承自AbstractDataSourceAdapter,实现了jdbc的DataSource,这里用到了适配器模式。 一张表经过分库分表后被拆分成多个子表,并分散到不同的数据库中,在不修改原业务 SQL 的前提下,shardingjdbc就必须对SQL进行一些改造才能正常执行。
大致的执行流程如下图,
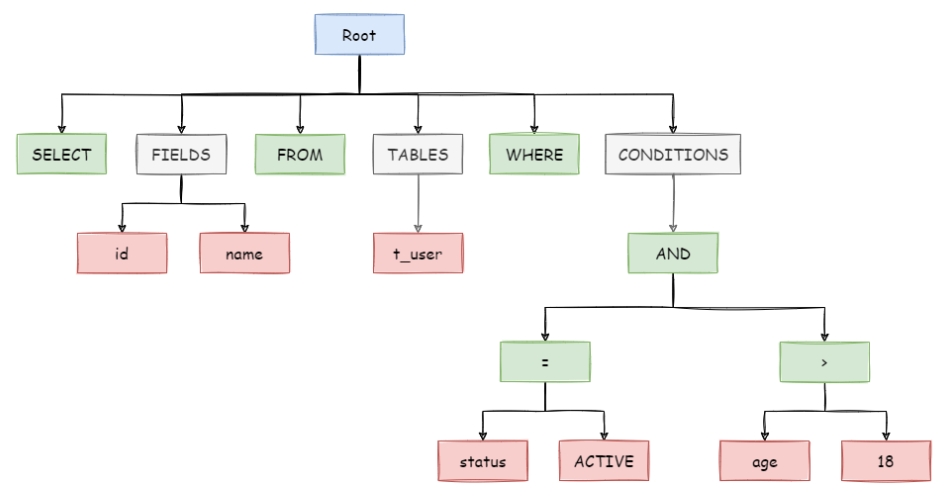
参考shardingsphere官方文档,sql语句会解析出一棵树,绿色是sql关键字,红色是sql中的变量,灰色是抽象的概念节点。
为什么要抽象成语法树呢?因为后面要查询优化、sql改写,需要先打散,后拼装。
sql改写的时候,是怎么知道要把逻辑sql中的逻辑表,改成成具体哪个物理表的呢?比如t_user改成t_user_0还是t_user_1呢?这就是sql路由的工作。
shardingjdbc的SQL路由原理
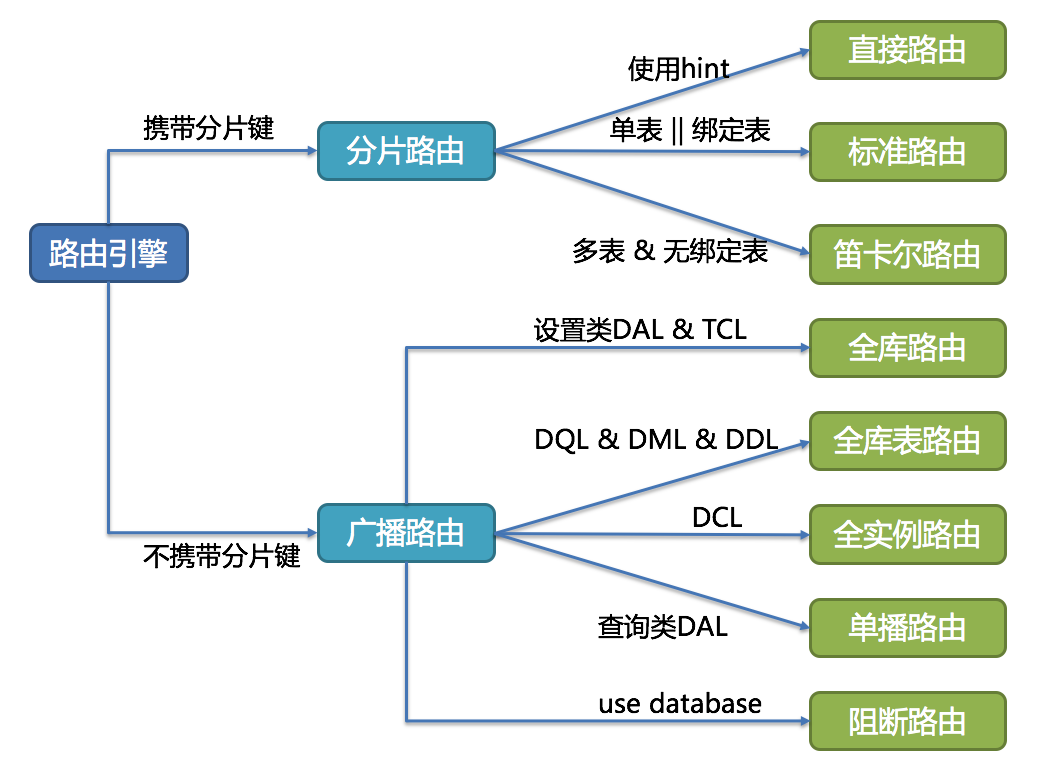
SQL路由通过解析分片上下文,匹配到用户配置的分片策略,并生成路由路径。
- 简单理解就是,可以根据我们配置的分片策略计算出
SQL该在哪个库的哪个表中执行; SQL路由又根据有无分片键,区分出分片路由和广播路由;- 路由规则,和
SQL的类型有很大关系。
SQL大概有哪些类型?(sql-parser-statement)
DQL(select)DML(update、insert、modify、delete)DDL(create、alter、drop、truncate、rename、comment)DCL(grant、revoke)TCL(commit、rollback、savePoint、setTransaction)DAL(describe、Kill、repair、use)
有分片键的路由叫分片路由,细分为直接路由、标准路由和笛卡尔积路由这3种类型。
无分片键的路由又叫做广播路由,可以划分为全库表路由、全库路由、 全实例路由、单播路由和阻断路由这5种类型。
- 标准路由
- 在精准路由策略下有俩条件,运算符是等号,查询的是分片键;如果条件关键字是非分片键,就不是标准路由了。精准路由策略的结果是定位到单库单表。
- 在范围路由下,和精准路由不一样的是,结果定位到多个分片,一条逻辑
sql会转变为多个真实的sql来执行。 - 两种场景,一种是单表查询,一种是多表查询,表和表之间是绑定表关系。
- 笛卡尔积路由
- 专门针对多表查询来的,做多表查询,表和表之间不是绑定表关系,就会产生笛卡尔积路由。
- 单播路由
- 虽然没有带分片键,现在要查询一个表的信息,比如查
t_order表的数据,它有多个物理表,这时只会找一个分片去查一个表的数据结构(字段信息)。 - 适合查询类的
DAL。
- 虽然没有带分片键,现在要查询一个表的信息,比如查
- 全库路由
- 在所有的数据源里边都执行一遍,只需要路由到库,不需要路由到表。
TCL(set autocommit=0)- 设置类
DAL
- 全库表路由
- 既要路由到库,又要路由到表
DQL&DML&DDL- 不带分片键,比如使用“用户名称”查询
- 全实例路由
- 数据库实例级别的操作
DCL
- 阻断路由
- 用来屏蔽
SQL对数据库的操作 use database;- 这个命令不会在真实数据库中执行,因为
ShardingSphere采⽤的是逻辑Schema(数据库的组织和结构)方式,所以无需将切换数据库的命令发送⾄真实数据库中。
- 用来屏蔽
官方文档
shouyuanman/sharding-jdbc-demo